|
Fudan University, China Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Fudan University, China
Inception Institute of Artificial Intelligence (IIAI), Abu Dhabi, UAE |
|
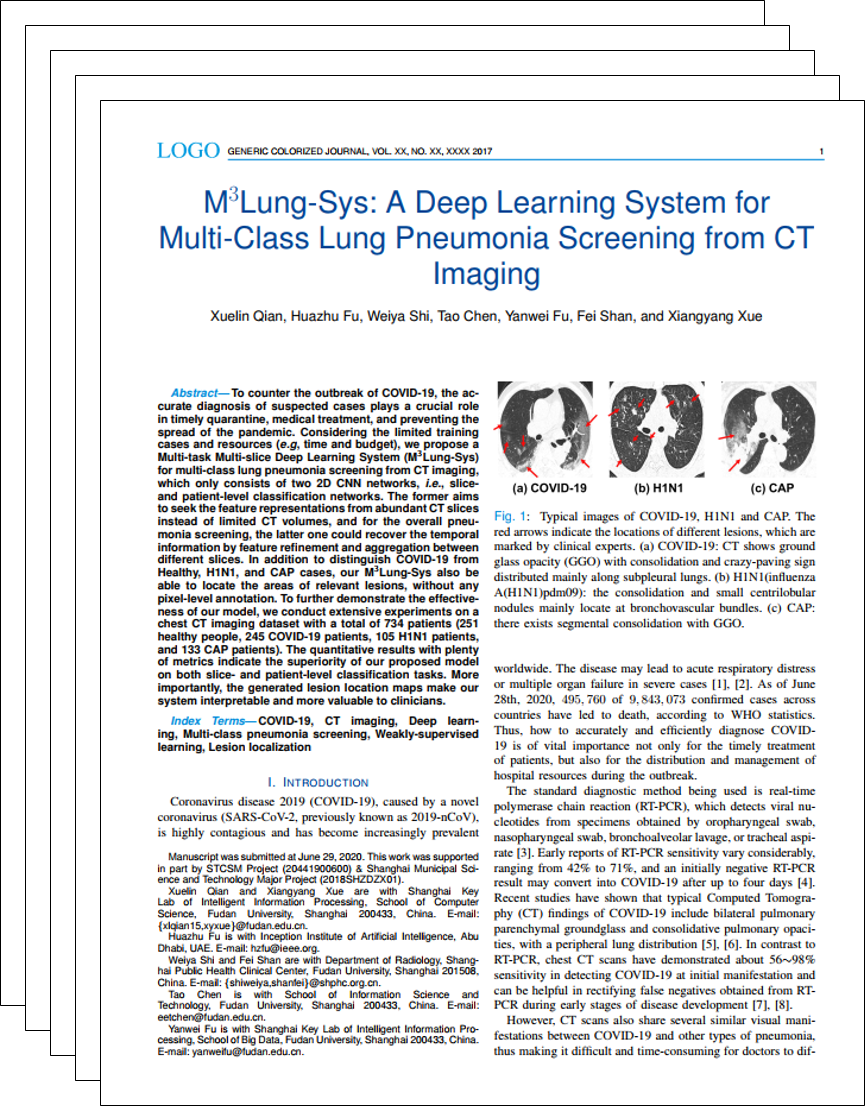
To counter the outbreak of COVID-19, the accurate diagnosis of suspected cases plays a crucial role
in timely quarantine, medical treatment, and preventing the spread of the pandemic. Considering the limited training cases and resources
(e.g, time and budget), we propose a Multi-task Multi-slice Deep Learning System (M3Lung-Sys) for multi-class lung pneumonia screening
from CT imaging, which only consists of two 2D CNN networks, i.e., sliceand patient-level classification networks. The former aims
to seek the feature representations from abundant CT slices instead of limited CT volumes, and for the overall pneumonia screening, the
latter one could recover the temporal information by feature refinement and aggregation between different slices. In addition to
distinguish COVID-19 from Healthy, H1N1, and CAP cases, our M3Lung-Sys also be able to locate the areas of relevant lesions, without any
pixel-level annotation. To further demonstrate the effectiveness of our model, we conduct extensive experiments on a chest CT imaging
dataset with a total of 734 patients (251 healthy people, 245 COVID-19 patients, 105 H1N1 patients, and 133 CAP patients). The quantitative
results with plenty of metrics indicate the superiority of our proposed model on both slice- and patient-level classification tasks. More
importantly, the generated lesion location maps make our system interpretable and more valuable to clinicians.
|
|
The Ethics Committee of Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Fudan University
approved the protocol of this study and waived the requirement for patient-informed consent (YJ-2020-S035-01).
A search through the medical records in our hospital information system was conducted, with the final dataset
consisting of 245 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, 105 patients with H1N1 pneumonia, 133 patients with CAP and
251 healthy subjects with non-pneumonia. Of the 734 enrolled people with 415 (56.5%) men, the mean age was
41.8±15.9 years (range, 2 ~ 96 years).
|
|
The proposed Multi-task Multi-slice Deep Learning System (M3Lung-Sys) consists
of two components, the Image Preprocessing and Classification Network.
|
|
M3Lung-Sys Framework
|
|
Specifically, the Image Preprocessing receives
raw CT exams, and prepare them for model training or inference. For the Classification Network, we
divide it into two subnets (stages), i.e., slice-level and patient-level classification networks, with the purpose of
jointly COVID-19 screening and location.Slice-level classification network is trained with multiple CT slice images and predicts
the corresponding slice-level categories, i.e., Healthy, COVID-19, H1N1 or CAP. Besides, patient-level classification
network only has four layers, and takes a volume of CT slice features, instead of images as input, which are extracted
by the former network, to output the patient-level labels. Both classification networks are trained separately due to
different tasks, but can be used concurrently in an end-to-end manner for the efficiency. More importantly, for cases
classified as positive (i.e., COVID-19, H1N1 or CAP), our system can locate suspected area of abnormality without any
pixel-level annotations.
|
|
The visualizations of our system outputs for one COVID-19 patient. We show a CT
sequence by sampling every five slices. The lesion location maps, with the predicted slicelevel diagnosis on the
upper right, are attached at the bottom of the corresponding raw CT slices. At the end of the sequence, the
probability of each category, predicted by the patient-level classification network is provided, i.e., 0: Healthy;
1: COVID-19; 2: H1N1; 3: CAP.
|
|
M3Lung-Sys: A Deep Learning System for Multi-Class Lung Pneumonia Screening from CT Imaging
Xuelin Qian, Huazhu Fu, Weiya Shi, Tao Chen, Yanwei Fu*, Fei Shan, and Xiangyang Xue [Paper] [Bibtex] |
Acknowledgements
The website is modified from this template.
|